Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Neurons, Neurotransmitters, Nerve Impulse, Conduction of Nerve Impulse, Synaptic Knob, Resting Potential, Generation of Nerve Impulse and, Transmission of Impulse at a Synapse
Important Questions on Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
What is synapse?
Two neurons, and , synapse onto a third neuron, . If neurotransmitter from A opens ligand-gated channels permeable to and and neurotransmitter from opens ligand-gated channels, which of the following statements is true?
Which event of the nerve impulse is indicated by the number (5) in the diagram?
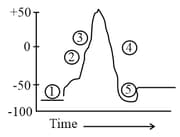
The resting axonal membrane is
Synaptic knob contains synaptic vesicles which possess chemicals called
The gaps between two adjacent myelin sheaths are called nodes of
Unmyelinated nerve fibres are found in
Neuron is a structure composed of three major parts, such as cell body, and axon.
Neuron can
Neurofibrils are the characteristic feature of
Nissl's granules are the characteristic feature of
Nissl's granules are actively participated in
Nissl's granules are
Nissl's granules are found in all except
Resting membrane potential of a neuron is approximately
Which event causes depolarisation of a neuron?
Mark the incorrect statement with respect to resting membrane potential:
Read the statements and find the correct option:
I. Resting the axonal membrane is almost impermeable to Na-ions and K-ions.
II. A polarised membrane, upon receiving the stimulus, becomes depolarised, and rapid efflux of NA-ion takes place.
III. The duration of stimulus-induced change of permeability for NA-ion is very short-lived.
IV. Repolarisation occurs only when there is an efflux of K-ions.
Each neuron has a cell body, axon, and dendrites. The dendrites are the protoplasmic extensions of the nerve cell. The axodendritic type of chemical synapse is formed by the association between the axon terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron and the dendrites of a post-synaptic neuron. The action potential causes the fusion of the synaptic vesicle to release the neurotransmitters for neurotransmission. Select the correct option from the following.
Potential difference across the resting membrane is negatively charged. This is due to differential distribution of the following ions:
